www.industryemea.com
06
'26
Written on Modified on
Intralogistics: Automated Readers & Traceability Solutions for Conveyors
How automatic readers on conveyor systems facilitate traceability in intralogistics.

Smart warehouse conveyor belt system with digital interface. Image: AI generated by Freepik
The global supply chains today have grown into a complex machinery with a million levers operating in perfect synchronisation, popping out packages with boring regularity. However, even this marvel of coordination can be thrown into a disarray owing to a host of factors, not all of which are under human control. While the occasional gremlin in the entire gamut of automation and digital technologies that facilitate this gigantic machinery is a risk always dangling and can be attributed to human error, factors beyond control are those too recent to be forgotten – the Covid-19 pandemic, rising geopolitical tensions, the 2021 Suez Canal blockage and the ongoing spectre of trade sanctions casting that shadow of recurring uncertainty.
At the heart of the perfect synchronisation that facilitates the complex intralogistics operations – the backbone of modern supply chains – is traceability, a critically important technology that provides essential visibility to track products from origin to consumer. Traceability is not merely about the smooth functioning of the supply chain. It involves quality and safety. It is about adhering to all the strict regulations, especially in the food/pharma industries where perishable and temperature sensitive products are handled. It is about customer confidence and trust, and the built-in response mechanism to instantly react to issues like defect detection and recall, further enhancing operational efficiency. Traceability today concerns the all important aspect of sustainability, ethical sourcing and environmental compliance, as the world increasingly tries to adopt a circular economy. It is about transforming complex global supply chains into transparent, manageable systems, reducing risks and costs while boosting overall service quality.
Automated readers and identification technologies
Traceability solutions comprise three core components: automated readers or automatic identification (Auto-ID) technologies, a centralised software system for data management, and the physical automation and hardware that move the goods.
The focus of this article is on the first component, i.e., automated readers in general, and how these are integrated on conveyor systems in intralogistic operations.
Automated readers are devices that identify, capture, and interpret coded data from product tags without human intervention. The most common types include:
The global supply chains today have grown into a complex machinery with a million levers operating in perfect synchronisation, popping out packages with boring regularity. However, even this marvel of coordination can be thrown into a disarray owing to a host of factors, not all of which are under human control. While the occasional gremlin in the entire gamut of automation and digital technologies that facilitate this gigantic machinery is a risk always dangling and can be attributed to human error, factors beyond control are those too recent to be forgotten – the Covid-19 pandemic, rising geopolitical tensions, the 2021 Suez Canal blockage and the ongoing spectre of trade sanctions casting that shadow of recurring uncertainty.
At the heart of the perfect synchronisation that facilitates the complex intralogistics operations – the backbone of modern supply chains – is traceability, a critically important technology that provides essential visibility to track products from origin to consumer. Traceability is not merely about the smooth functioning of the supply chain. It involves quality and safety. It is about adhering to all the strict regulations, especially in the food/pharma industries where perishable and temperature sensitive products are handled. It is about customer confidence and trust, and the built-in response mechanism to instantly react to issues like defect detection and recall, further enhancing operational efficiency. Traceability today concerns the all important aspect of sustainability, ethical sourcing and environmental compliance, as the world increasingly tries to adopt a circular economy. It is about transforming complex global supply chains into transparent, manageable systems, reducing risks and costs while boosting overall service quality.
Automated readers and identification technologies
Traceability solutions comprise three core components: automated readers or automatic identification (Auto-ID) technologies, a centralised software system for data management, and the physical automation and hardware that move the goods.
The focus of this article is on the first component, i.e., automated readers in general, and how these are integrated on conveyor systems in intralogistic operations.
Automated readers are devices that identify, capture, and interpret coded data from product tags without human intervention. The most common types include:
- Barcode scanners (1D and 2D)
- RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) readers (fixed and handheld)
- Vision systems (machine vision cameras), and
- Laser scanners and OCR (Optical Character Recognition).
These readers are often positioned along conveyors to automatically scan items as they pass through key checkpoints.
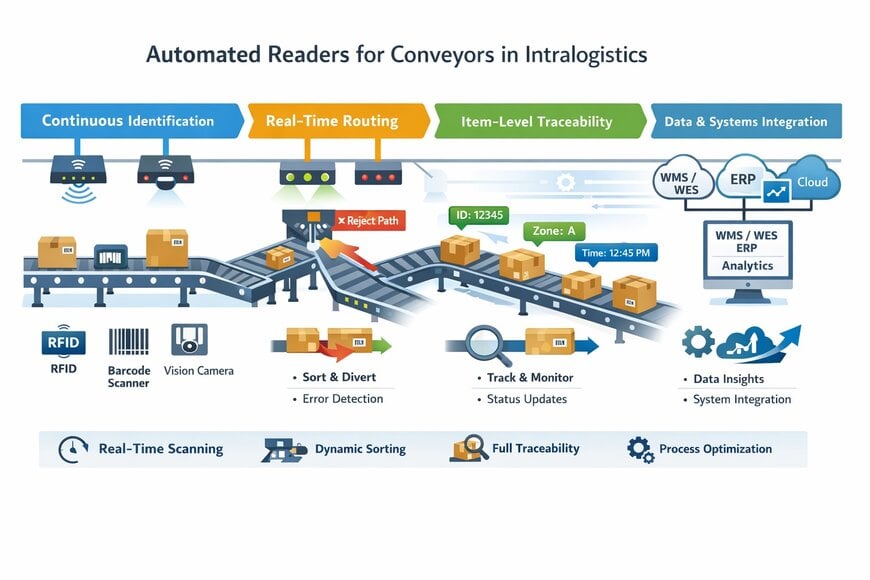
AI-generated infographic showing automated readers for conveyors
Traceability: The backbone of modern intralogistics
Traceability is the ability to track and trace products and materials throughout the internal logistics process. It ensures visibility at every stage – from inbound receiving and put-away to order picking, packing, and outbound shipping.
Robust traceability enables:

AI-generated infographic showing automated readers for conveyors
Traceability: The backbone of modern intralogistics
Traceability is the ability to track and trace products and materials throughout the internal logistics process. It ensures visibility at every stage – from inbound receiving and put-away to order picking, packing, and outbound shipping.
Robust traceability enables:
- Real-time inventory visibility
- Error reduction (e.g., mispicks, wrong shipments)
- Compliance with regulations and audits
- Root-cause analysis for quality or process failures, and
- Seamless integration with Warehouse Management Systems (WMS), ERP, and MES.
Without traceability, warehouses cannot guarantee the accuracy, speed, or accountability expected in modern supply chains.
The role of conveyors in intralogistics
Conveyors are the arteries of material flow in large facilities. They transport cartons, totes, pallets, and other units between:
The role of conveyors in intralogistics
Conveyors are the arteries of material flow in large facilities. They transport cartons, totes, pallets, and other units between:
- Receiving docks
- Sorting areas
- Buffer zones
- Picking stations
- Packing and labelling stations, and
- Shipping docks.
High-throughput conveyors move thousands of units per hour. However, without effective identification and traceability, this flow becomes blind and unmanageable – leading to inefficiencies, bottlenecks, and errors.
Integrating automated readers with conveyors
Automated readers transform static conveyor belts into intelligent checkpoints. When strategically placed, they provide real-time data that feeds operational decisions. Key integration points include:
1. Inbound receiving
At inbound checkpoints, barcode or RFID readers automatically capture the identity of incoming pallets or cartons. This enables:
Integrating automated readers with conveyors
Automated readers transform static conveyor belts into intelligent checkpoints. When strategically placed, they provide real-time data that feeds operational decisions. Key integration points include:
1. Inbound receiving
At inbound checkpoints, barcode or RFID readers automatically capture the identity of incoming pallets or cartons. This enables:
- Immediate confirmation of goods received vs. purchase orders
- Early detection of discrepancies,
- Automated put-away instructions.
2. Sortation points
As items travel along the conveyor, readers trigger downstream actions:
As items travel along the conveyor, readers trigger downstream actions:
- Diverting to correct lanes
- Routing based on order priorities, and
- Feeding sortation algorithms in real time.
Here, high-speed tunnel scanners or RFID portals ensure accuracy even at high conveyor speeds.
3. Quality checkpoints
Vision systems and OCR readers verify labels, detect damage, or confirm product attributes. If a defect is detected, conveyors can automatically divert items to inspection or rework lanes without human intervention.
4. Outbound shipping
Final readers confirm that sorted and packed orders match outbound bills of lading. This ensures correct shipments every time and avoids costly returns or penalties.
Automated readers: Barcode vs. RFID
Both barcode and RFID technologies are widely used, but their strengths vary.
Features of barcode readers:
3. Quality checkpoints
Vision systems and OCR readers verify labels, detect damage, or confirm product attributes. If a defect is detected, conveyors can automatically divert items to inspection or rework lanes without human intervention.
4. Outbound shipping
Final readers confirm that sorted and packed orders match outbound bills of lading. This ensures correct shipments every time and avoids costly returns or penalties.
Automated readers: Barcode vs. RFID
Both barcode and RFID technologies are widely used, but their strengths vary.
Features of barcode readers:
- Low cost
- High accuracy
- Require line-of-sight, and
- Best for carton-level identification.
In conveyor systems, fixed-position barcode scanners can rapidly read 1D/2D labels printed on cartons. They are ideal where labelling is consistent and predictable.
Features of RFID readers:
Features of RFID readers:
- No line-of-sight required
- Can read multiple tags simultaneously
- Higher initial costs, and
- More robust in harsh environments.
RFID is especially powerful for pallet tracking, returnable totes, and high-density zones where barcode readability might be compromised.
Often, modern intralogistics environments use a hybrid approach – barcode scanning for individual unit verification and RFID for bulk inventory movement.
Traceability solutions: Beyond simple scanning
Automated readers are only as effective as the systems they feed. A modern traceability solution typically includes:
1. Real-Time Location Systems (RTLS)
RTLS leverages RFID or UWB (Ultra-Wideband) to track the precise location of assets (e.g., AGVs, pallets, containers) on the conveyor network. This allows dynamic routing and labelling based on real-time conditions.
2. Middleware Platforms
Middleware sits between the hardware (readers, conveyors) and enterprise systems (WMS/ERP). It handles:
Often, modern intralogistics environments use a hybrid approach – barcode scanning for individual unit verification and RFID for bulk inventory movement.
Traceability solutions: Beyond simple scanning
Automated readers are only as effective as the systems they feed. A modern traceability solution typically includes:
1. Real-Time Location Systems (RTLS)
RTLS leverages RFID or UWB (Ultra-Wideband) to track the precise location of assets (e.g., AGVs, pallets, containers) on the conveyor network. This allows dynamic routing and labelling based on real-time conditions.
2. Middleware Platforms
Middleware sits between the hardware (readers, conveyors) and enterprise systems (WMS/ERP). It handles:
- Data filtering and normalisation
- Event management, and
- Intelligence for exception handling.
This prevents the WMS from being overwhelmed with raw reads and duplicates.
3. Integration with WMS and Conveyor Control Systems
With seamless integration:
3. Integration with WMS and Conveyor Control Systems
With seamless integration:
- WMS knows the exact status of every carton
- Conveyor control logic can adjust speeds, sortation, or holds based on status, and
- Alerts and KPIs propagate to dashboards.
This closed-loop system ensures operational transparency and agility.
Key benefits of automated readers & traceability in conveyor systems
1. Higher Throughput with Fewer Errors: Automated scanning eliminates manual touch points. Conveyor zones equipped with readers capture every unit as it flows – no delays, no missed scans.
2. Real-Time Inventory Accuracy: Every read updates inventory instantly. This minimises discrepancies between physical stock and system records – critical for real-time decision making.
3. Enhanced Sortation and Routing: With traceability data, conveyor systems can make dynamic routing decisions – rebalancing loads, preventing congestion, and optimising flows.
4. Faster Order Fulfillment: Accurate identification combined with automated conveyors accelerates picking, packing, and shipping cycles.
5. Better Traceability and Compliance: In sectors like food & beverage, pharma, and electronics, traceability is regulated. Automated systems create tamper-proof audit trails.

Dematic Multishuttle 2 – shuttle-based automated storage and retrieval system (AS/RS). Image source: Dematic
Challenges and considerations
While the benefits are compelling, deploying automated readers and traceability solutions also presents challenges:
1. Tag and Label Quality: Poor label quality (smudged barcodes, low-contrast printing) can cause misreads. Ensuring high-quality labelling is essential.
2. Environment and Speed: Dust, lighting conditions, and high conveyor speeds can impact read performance. This requires careful selection and calibration of sensors.
3. Data Overload: High read volumes can overwhelm systems. Intelligent filtering through middleware is necessary to process meaningful events.
4. Interference and Tag Collision: In RFID environments, tag collisions (multiple tags read simultaneously) and metal interference can occur. Proper frequency planning and antenna placement mitigate this.
5. Integration Complexity: Connecting readers, conveyor PLCs, WMS, and control systems requires robust architecture and often custom interfaces.
Top vendors of traceability solutions for conveyors in intralogistics
1. Dematic (KION Group): One of the largest global providers of smart material handling and automation systems – including conveyors with integrated tracking technologies and warehouse control/visibility software.
2) Daifuku Co., Ltd: A leading intralogistics and conveyor systems supplier that delivers fully integrated automation solutions with item traceability, sorting and tracking across conveyor networks.
3) Swisslog (KUKA Group): Delivers comprehensive automated material handling and logistics solutions – conveyors, robotics, WMS/WCS software with high traceability, RFID and data analytics for real-time product visibility.
4) Honeywell Intelligrated: Offers advanced conveyor systems with integrated software for visibility and tracking, including data capture at key process points in the warehouse.
5) SSI Schaefer: Modular conveyor systems paired with warehouse software that supports traceability via RFID/barcode scanning and integration with enterprise systems.
6) TGW Logistics Group: Provides automated conveyors with integrated control and software layers that can manage and track material flows throughout operations.
7) BOWE Intralogistics: Delivers intralogistics systems with IoT and sensor technologies (RFID, barcodes) that ensure product traceability across conveyors and sortation processes.
8) Turck Vilant Systems: Specialises in turnkey RFID-based track-and-trace platforms that can be deployed across conveyor checkpoints, inventory nodes, and forklift/handling zones.
9) Impinj: Provides RAIN RFID platforms and ecosystem partners that enable automated item identification and tracking on conveyors and in storage/handling flows – especially effective for high-speed logistics operations.
10) Lyngsoe Systems: Offers RFID/RTLS solutions integrated with warehouse systems to provide continuous visibility and traceability across conveyor and material handling equipment.

Turck Vilant Systems provides turnkey RFID solutions for production logistics. Image source: Turck
Future trends in conveyor traceability
With the rapid evolution of digital technologies, exciting possibilities are in store for conveyor traceability solutions. For example, AI and machine vision are increasingly used not just to identify codes, but also detect package orientation, label quality, and even product conditions. Similarly, sensors on conveyors, besides measuring vibration, load, or belt condition, will also contribute to analytics that predict maintenance needs and reduce downtime.
Another promising development is that edge processors can filter and preprocess reads near the source, reducing latency and bandwidth requirements for central systems. Finally, digital representations of conveyor networks will facilitate real time updates with traceability data, enabling simulation and optimisation without disrupting operations.
Conclusion: A connected conveyor ecosystem
Automated readers and traceability solutions are no longer optional add-ons – they are core components of intelligent intralogistics ecosystems. When effectively integrated with conveyor systems, they turn passive material flow into an orchestrated, data-driven process that improves accuracy, speed, and responsiveness.
For today’s high-volume, high-variability warehouses, these technologies are essential foundations for agility, scalability, and competitive advantage in a world where every second and every scan counts. If intralogistics is the backbone of modern supply chains, traceability is the backbone of modern intralogistics operation.
Key benefits of automated readers & traceability in conveyor systems
1. Higher Throughput with Fewer Errors: Automated scanning eliminates manual touch points. Conveyor zones equipped with readers capture every unit as it flows – no delays, no missed scans.
2. Real-Time Inventory Accuracy: Every read updates inventory instantly. This minimises discrepancies between physical stock and system records – critical for real-time decision making.
3. Enhanced Sortation and Routing: With traceability data, conveyor systems can make dynamic routing decisions – rebalancing loads, preventing congestion, and optimising flows.
4. Faster Order Fulfillment: Accurate identification combined with automated conveyors accelerates picking, packing, and shipping cycles.
5. Better Traceability and Compliance: In sectors like food & beverage, pharma, and electronics, traceability is regulated. Automated systems create tamper-proof audit trails.

Dematic Multishuttle 2 – shuttle-based automated storage and retrieval system (AS/RS). Image source: Dematic
Challenges and considerations
While the benefits are compelling, deploying automated readers and traceability solutions also presents challenges:
1. Tag and Label Quality: Poor label quality (smudged barcodes, low-contrast printing) can cause misreads. Ensuring high-quality labelling is essential.
2. Environment and Speed: Dust, lighting conditions, and high conveyor speeds can impact read performance. This requires careful selection and calibration of sensors.
3. Data Overload: High read volumes can overwhelm systems. Intelligent filtering through middleware is necessary to process meaningful events.
4. Interference and Tag Collision: In RFID environments, tag collisions (multiple tags read simultaneously) and metal interference can occur. Proper frequency planning and antenna placement mitigate this.
5. Integration Complexity: Connecting readers, conveyor PLCs, WMS, and control systems requires robust architecture and often custom interfaces.
Top vendors of traceability solutions for conveyors in intralogistics
1. Dematic (KION Group): One of the largest global providers of smart material handling and automation systems – including conveyors with integrated tracking technologies and warehouse control/visibility software.
2) Daifuku Co., Ltd: A leading intralogistics and conveyor systems supplier that delivers fully integrated automation solutions with item traceability, sorting and tracking across conveyor networks.
3) Swisslog (KUKA Group): Delivers comprehensive automated material handling and logistics solutions – conveyors, robotics, WMS/WCS software with high traceability, RFID and data analytics for real-time product visibility.
4) Honeywell Intelligrated: Offers advanced conveyor systems with integrated software for visibility and tracking, including data capture at key process points in the warehouse.
5) SSI Schaefer: Modular conveyor systems paired with warehouse software that supports traceability via RFID/barcode scanning and integration with enterprise systems.
6) TGW Logistics Group: Provides automated conveyors with integrated control and software layers that can manage and track material flows throughout operations.
7) BOWE Intralogistics: Delivers intralogistics systems with IoT and sensor technologies (RFID, barcodes) that ensure product traceability across conveyors and sortation processes.
8) Turck Vilant Systems: Specialises in turnkey RFID-based track-and-trace platforms that can be deployed across conveyor checkpoints, inventory nodes, and forklift/handling zones.
9) Impinj: Provides RAIN RFID platforms and ecosystem partners that enable automated item identification and tracking on conveyors and in storage/handling flows – especially effective for high-speed logistics operations.
10) Lyngsoe Systems: Offers RFID/RTLS solutions integrated with warehouse systems to provide continuous visibility and traceability across conveyor and material handling equipment.

Turck Vilant Systems provides turnkey RFID solutions for production logistics. Image source: Turck
Future trends in conveyor traceability
With the rapid evolution of digital technologies, exciting possibilities are in store for conveyor traceability solutions. For example, AI and machine vision are increasingly used not just to identify codes, but also detect package orientation, label quality, and even product conditions. Similarly, sensors on conveyors, besides measuring vibration, load, or belt condition, will also contribute to analytics that predict maintenance needs and reduce downtime.
Another promising development is that edge processors can filter and preprocess reads near the source, reducing latency and bandwidth requirements for central systems. Finally, digital representations of conveyor networks will facilitate real time updates with traceability data, enabling simulation and optimisation without disrupting operations.
Conclusion: A connected conveyor ecosystem
Automated readers and traceability solutions are no longer optional add-ons – they are core components of intelligent intralogistics ecosystems. When effectively integrated with conveyor systems, they turn passive material flow into an orchestrated, data-driven process that improves accuracy, speed, and responsiveness.
For today’s high-volume, high-variability warehouses, these technologies are essential foundations for agility, scalability, and competitive advantage in a world where every second and every scan counts. If intralogistics is the backbone of modern supply chains, traceability is the backbone of modern intralogistics operation.
Article contributed by Milton D'Silva, a freelance technical writer, and former editor of Industrial Products Finder, India.

