www.industryemea.com
02
'25
Written on Modified on
How Blue Laser Technology is Transforming 3D Scanning
Blue laser 3D scanning from Photoneo delivers up to 2.5× greater data completeness, improved detection of difficult materials, and seamless multi-sensor integration.
www.photoneo.com
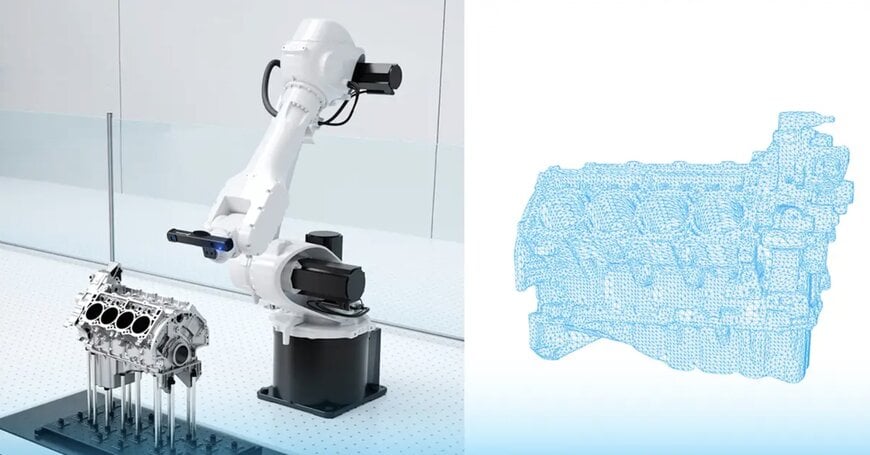
When we first came up with the idea to enhance our projection units with the power of blue light wavelengths, we knew we were onto something extraordinary.
Today, we can confidently say that the new generation of 3D scanners delivers 2.5x better data completeness and 50% more scanning power, while offering the ability to be conveniently paired with red laser systems in multi-sensor setups for simultaneous, interference-free 3D scanning tasks – essential for applications like bin picking and 3D meshing.
By solving long-standing challenges with difficult materials, extending scanning ranges, and enabling new multi-sensor configurations, blue laser vision systems are opening up application areas that were previously impractical or impossible.
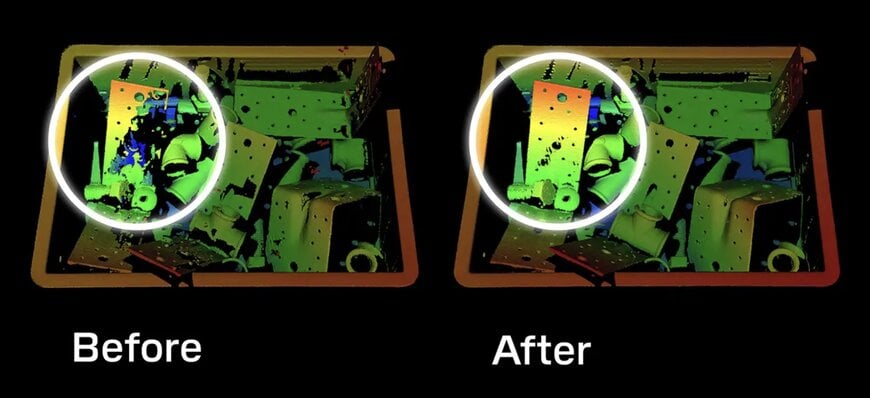
The Physics Behind the Blue Laser Advantage
To understand why blue laser technology represents such a significant advancement, we need to dive into the fundamental physics of light interaction with materials. The key lies in wavelength.
Blue lasers typically operate at wavelengths around 405-450 nanometers, significantly shorter than the 650-670 nanometer wavelengths of traditional red lasers.
This shorter wavelength brings several crucial advantages.
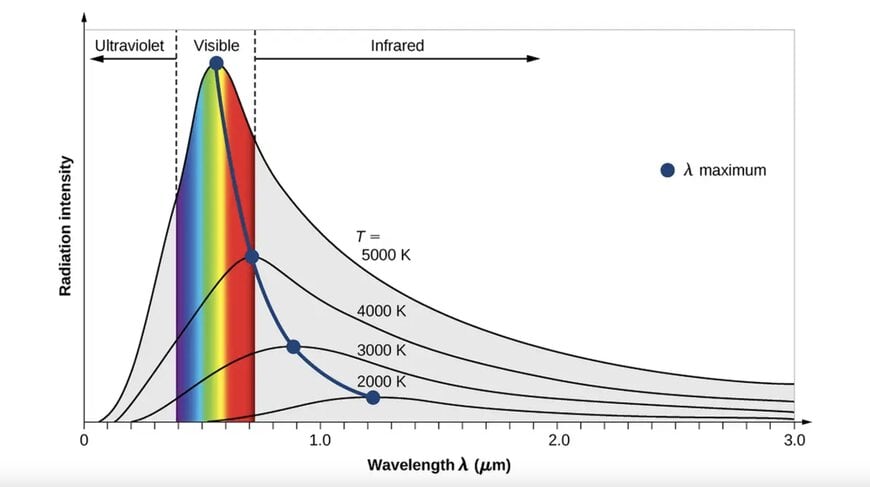
Enhanced Surface Interaction
Shorter wavelengths scatter more effectively across a broader range of materials. This phenomenon means that blue light interacts more readily with surface textures and microscopic irregularities that longer wavelengths might pass through or reflect away from.
The result is dramatically improved data capture on challenging materials that have historically been problematic for 3D scanning.
Reduced Speckle Noise
One of the most significant technical improvements blue lasers bring is the reduction of speckle noise.
Speckle patterns – those granular interference patterns that appear when coherent light reflects off rough surfaces – have long been a nemesis of precision 3D scanning.
The finer speckle structure produced by blue lasers creates less interference with captured data, resulting in cleaner, more accurate point clouds.
Superior Signal-to-Noise Ratio
Blue laser vision systems can achieve higher signal-to-noise ratios, particularly when combined with sensors optimized for blue wavelengths.
This improvement translates directly into better data quality, especially in challenging scanning conditions where ambient light or material properties might compromise measurement accuracy.
Breaking Through Material Barriers
Perhaps nowhere is the advantage of blue laser technology more apparent than in its ability to handle materials that have traditionally challenged 3D scanning systems.
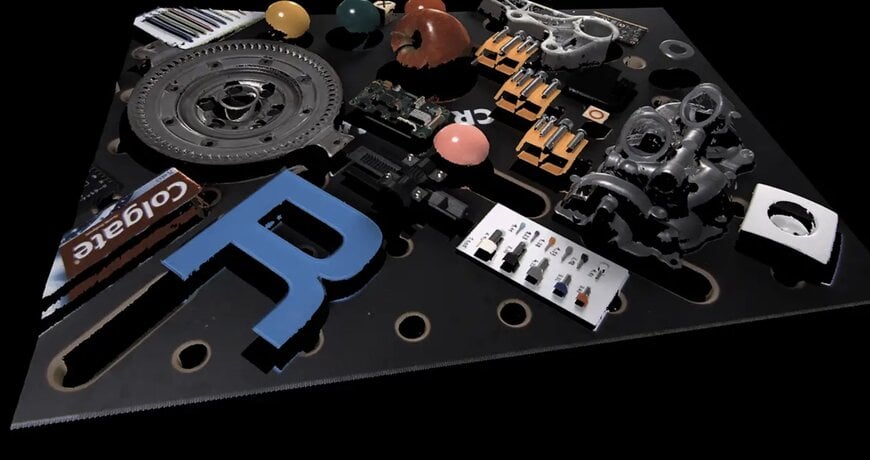

Reflective and Metallic Surfaces
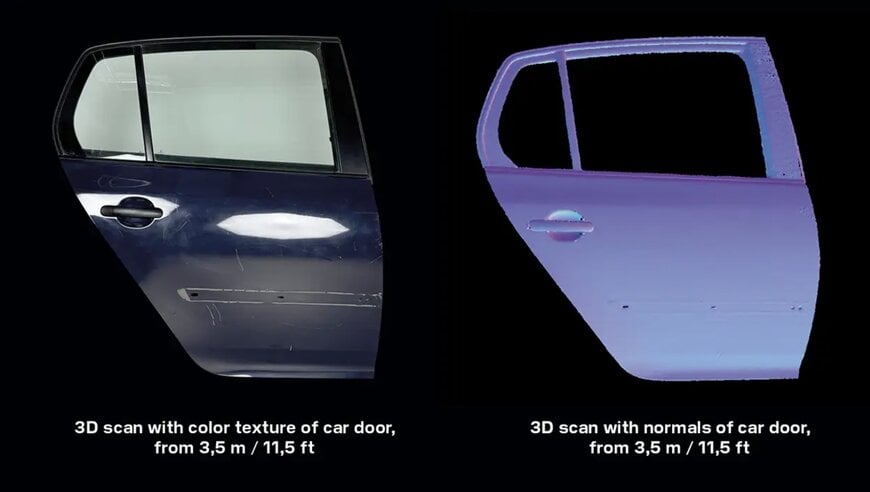
Automotive manufacturing, with its abundance of polished metal components, stamped parts, and reflective surfaces, has been a particularly challenging environment for traditional 3D scanning.
Blue lasers excel at penetrating through surface reflections and capturing meaningful geometric data from highly reflective materials.
This capability opens up new possibilities for in-line quality inspection of automotive components, from body panels to precision-machined engine parts.
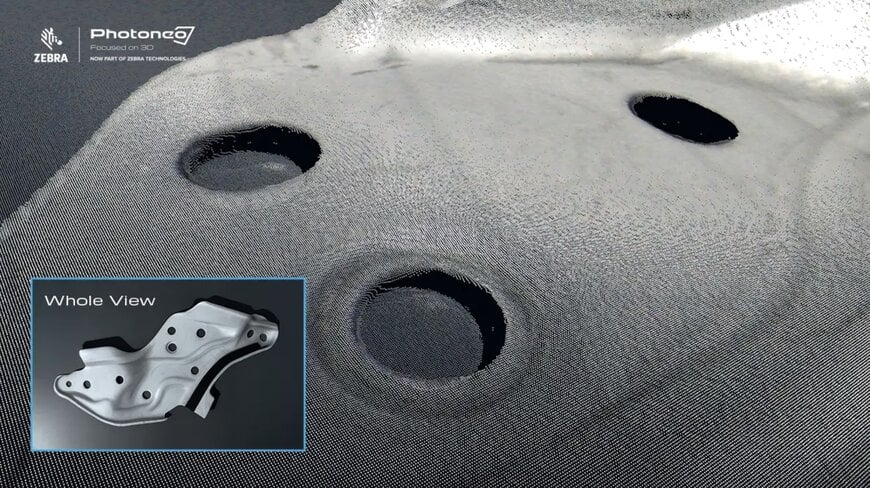

Reflective metal part from automotive industry – close up
Dark and Absorptive Materials
At the opposite end of the spectrum, very dark materials that absorb most incident light have also posed challenges for red laser systems.
The higher energy density and different absorption characteristics of blue light often allow for better reflection from these challenging surfaces, expanding the range of materials that can be reliably scanned without special surface treatments.
Transparent and Semi-Transparent Objects
One of the most exciting applications of blue laser technology is in scanning transparent and semi-transparent materials.
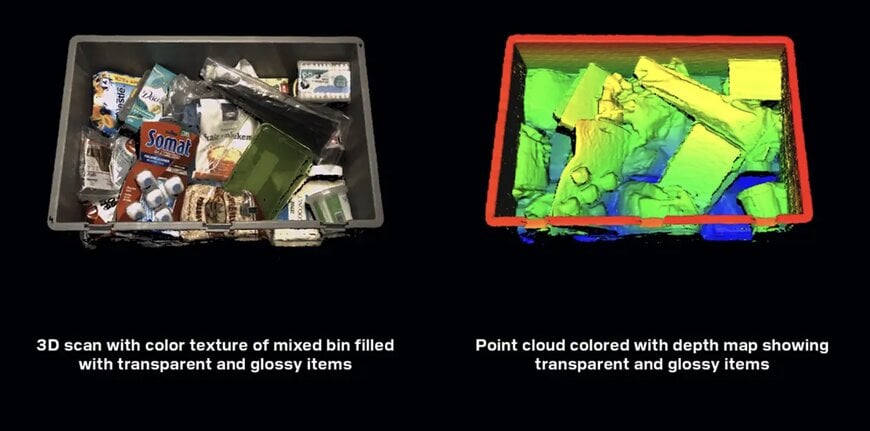
Automotive applications like gap and flush measurement between headlamps and body panels – where you’re essentially measuring the relationship between transparent plastic and painted metal – become feasible with blue laser systems in ways that weren’t practical with red light.
Extended Range Capabilities
Blue laser technology doesn’t just improve scanning quality at traditional ranges – it extends the useful scanning envelope significantly.
Several factors contribute to this enhanced range performance:
- Higher Power Density – Blue laser projection units can deliver significantly more optical power within the same laser safety class restrictions. This increased power density means a more useful signal reaches distant objects, enabling reliable data capture at ranges that would be marginal or impossible with red laser systems.
- Improved Dynamic Range – When combined with advanced sensors and processing algorithms, blue laser systems can achieve dynamic ranges 20dB or more beyond traditional systems. This extended dynamic range means the scanner can simultaneously capture fine details on nearby objects while still maintaining signal integrity from distant surfaces – a crucial capability for applications like palletizing, where robots might need to scan objects at various heights within a large working volume.
- Better Ambient Light Suppression – The spectral characteristics of blue lasers, combined with precisely matched optical filters, enable superior ambient light suppression. This capability is particularly valuable in industrial environments where natural lighting, overhead fluorescents, or other illumination sources might interfere with scanning operations.
Multi-Sensor Synergy
One of the most innovative applications of blue laser technology is in multi-sensor scanning configurations. Because blue and red wavelengths operate in distinct spectral bands, sensors using different laser colors can operate simultaneously without interference.

Red and Blue laser patterns on the same scene, no interference
This capability enables several powerful scanning modalities:
Parallel Multi-View Scanning
Rather than scanning sequentially from different angles – which adds time and complexity – blue and red laser systems can scan simultaneously from multiple perspectives.
This parallel operation cuts scanning time in half while providing the multiple viewpoints needed for complete object reconstruction.
Hand-eye vs Extrinsic 3D sensor setup for MultiView scanning
Complementary Material Coverage
Different laser wavelengths interact differently with various materials. By using both blue and red lasers simultaneously, scanning systems can optimize data capture across a broader range of surface types, essentially combining the strengths of both technologies.
Enhanced Robustness
Multi-wavelength scanning provides inherent redundancy. If one laser struggles with a particular surface or material characteristic, the other wavelength often compensates, resulting in more complete and reliable data capture.
Applications Transformed by Blue Laser Technology
The capabilities enabled by blue laser technology are opening up entirely new application areas and dramatically improving existing ones:
Advanced Quality Inspection
The improved resolution and material compatibility of blue laser systems enable quality inspection applications that were previously impractical.
Weld bead inspection, surface finish analysis, and dimensional verification of complex geometries all benefit from the enhanced data quality and completeness that blue lasers provide.

Outdoor and Variable Lighting Applications
Superior ambient light suppression makes blue laser systems viable for applications in uncontrolled lighting environments.
Solar panel inspection, agricultural applications, and railway maintenance – all scenarios where consistent artificial lighting isn’t practical – become feasible with robust blue laser scanning systems.
High-Precision Assembly Operations
In electronics manufacturing and other precision assembly operations, the improved resolution and material handling capabilities of blue laser systems enable more sophisticated guidance and verification tasks.
Component placement and quality verification can all be performed with higher confidence and accuracy.

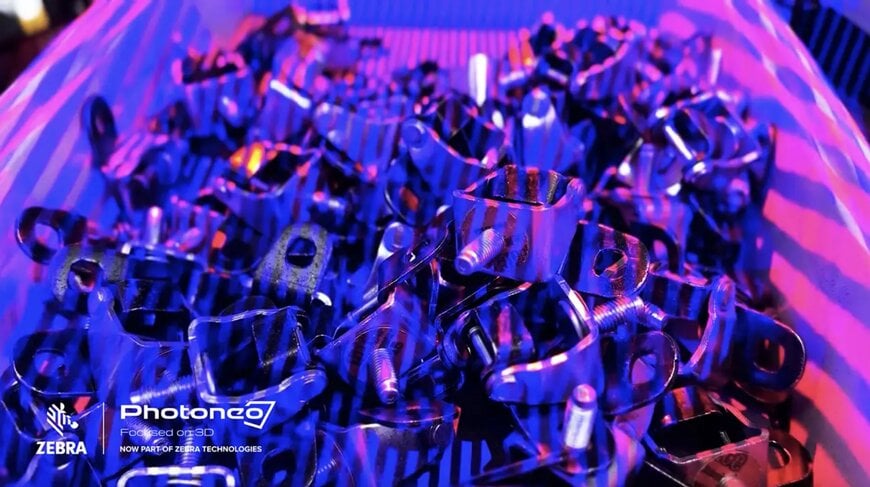
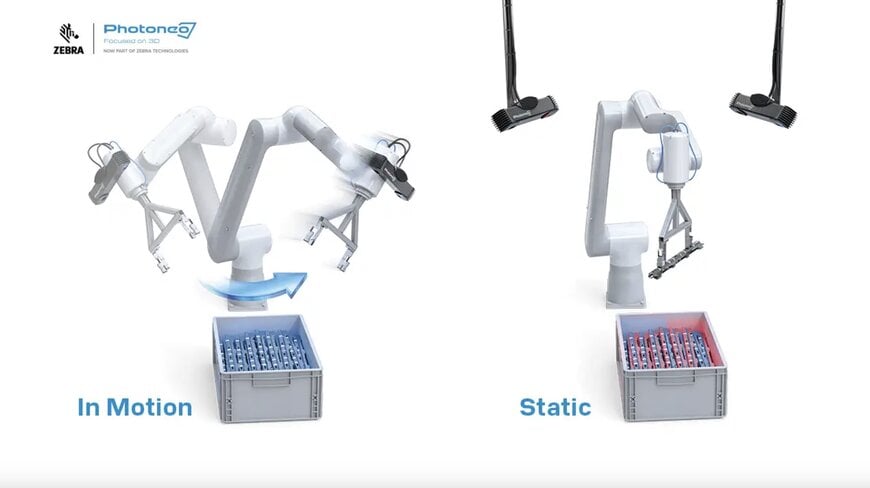
Precise Bin Picking with Blue Laser
Large-Scale Automation
The extended range capabilities of blue laser systems enable automation in larger working volumes. Warehouse automation, large-part manufacturing, and infrastructure inspection applications all benefit from the ability to capture high-quality data across greater distances.
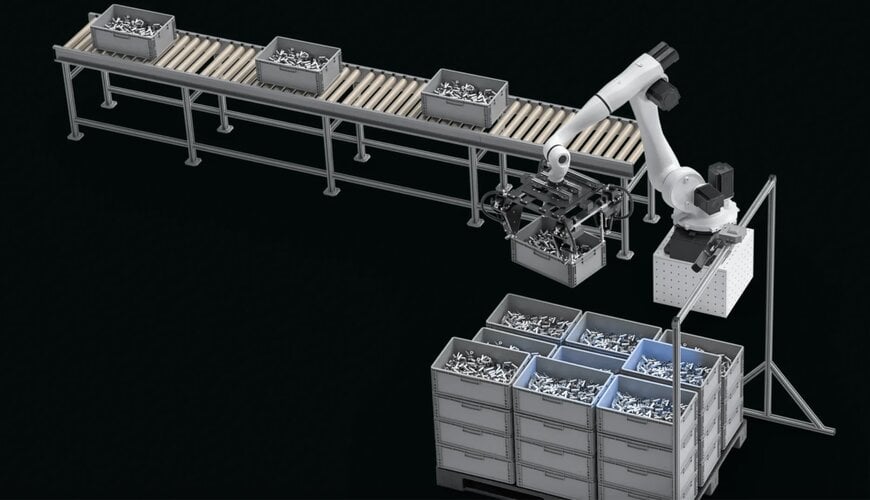

Depalletization / KLT manipulation
Looking Forward: The Future of Blue Laser Technology
As blue laser technology matures, we can expect to see continued improvements in several areas:
Integration with Artificial Intelligence
The higher quality, more complete data provided by blue laser systems creates better inputs for AI-powered analysis and decision-making systems. This synergy between improved sensing and intelligent processing will enable even more sophisticated automation applications.
Enhanced Multi-Modal Sensing
In future scenarios, the combination of blue laser structured light with other sensing modalities, such as thermal imaging, hyperspectral analysis, or advanced RGB processing, can create comprehensive sensing systems capable of unprecedented material analysis and geometric measurement.
Explore Photoneo’s Blue Laser devices – MotionCam-3D Color (Blue) for dynamic scanning in motion and PhoXi 3D Scanner Gen3 for the maximum precision in static scenes.
www.photoneo.com
One of the most innovative applications of blue laser technology is in multi-sensor scanning configurations. Because blue and red wavelengths operate in distinct spectral bands, sensors using different laser colors can operate simultaneously without interference.

Red and Blue laser patterns on the same scene, no interference
This capability enables several powerful scanning modalities:
Parallel Multi-View Scanning
Rather than scanning sequentially from different angles – which adds time and complexity – blue and red laser systems can scan simultaneously from multiple perspectives.
This parallel operation cuts scanning time in half while providing the multiple viewpoints needed for complete object reconstruction.

Hand-eye vs Extrinsic 3D sensor setup for MultiView scanning
Complementary Material Coverage
Different laser wavelengths interact differently with various materials. By using both blue and red lasers simultaneously, scanning systems can optimize data capture across a broader range of surface types, essentially combining the strengths of both technologies.
Enhanced Robustness
Multi-wavelength scanning provides inherent redundancy. If one laser struggles with a particular surface or material characteristic, the other wavelength often compensates, resulting in more complete and reliable data capture.
Applications Transformed by Blue Laser Technology
The capabilities enabled by blue laser technology are opening up entirely new application areas and dramatically improving existing ones:
Advanced Quality Inspection
The improved resolution and material compatibility of blue laser systems enable quality inspection applications that were previously impractical.
Weld bead inspection, surface finish analysis, and dimensional verification of complex geometries all benefit from the enhanced data quality and completeness that blue lasers provide.

Outdoor and Variable Lighting Applications
Superior ambient light suppression makes blue laser systems viable for applications in uncontrolled lighting environments.
Solar panel inspection, agricultural applications, and railway maintenance – all scenarios where consistent artificial lighting isn’t practical – become feasible with robust blue laser scanning systems.
High-Precision Assembly Operations
In electronics manufacturing and other precision assembly operations, the improved resolution and material handling capabilities of blue laser systems enable more sophisticated guidance and verification tasks.
Component placement and quality verification can all be performed with higher confidence and accuracy.

Precise Bin Picking with Blue Laser
Large-Scale Automation
The extended range capabilities of blue laser systems enable automation in larger working volumes. Warehouse automation, large-part manufacturing, and infrastructure inspection applications all benefit from the ability to capture high-quality data across greater distances.

Depalletization / KLT manipulation
Looking Forward: The Future of Blue Laser Technology
As blue laser technology matures, we can expect to see continued improvements in several areas:
Integration with Artificial Intelligence
The higher quality, more complete data provided by blue laser systems creates better inputs for AI-powered analysis and decision-making systems. This synergy between improved sensing and intelligent processing will enable even more sophisticated automation applications.
Enhanced Multi-Modal Sensing
In future scenarios, the combination of blue laser structured light with other sensing modalities, such as thermal imaging, hyperspectral analysis, or advanced RGB processing, can create comprehensive sensing systems capable of unprecedented material analysis and geometric measurement.
Explore Photoneo’s Blue Laser devices – MotionCam-3D Color (Blue) for dynamic scanning in motion and PhoXi 3D Scanner Gen3 for the maximum precision in static scenes.
www.photoneo.com

