www.industryemea.com
06
'13
Written on Modified on
Operating costs
Five ways to cut operating expenses on telecom infrastructure
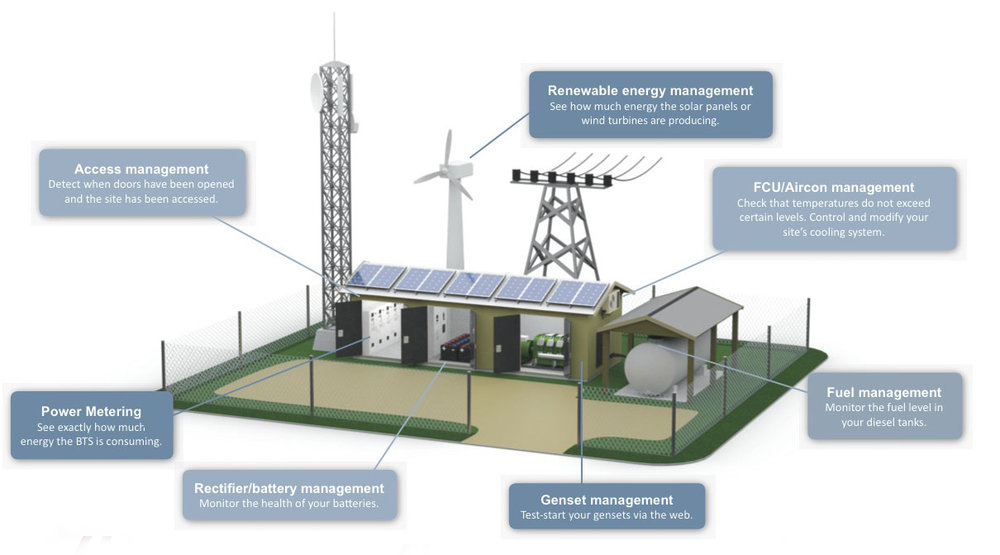
1) Energy metering – the key to making the right decisions.
By adding intelligent energy meters (sometimes referred as smart meters) at strategic locations in your base station, you will get a detailed overview of how much energy each part of your BTS is consuming. For example, with an AC meter installed directly after the mains, and DC meters which measure the consumption of the telecom load, you can easily calculate the site’s Energy Efficiency Ratio (EER).
Additionally, energy meters can be added to individual equipment (the air-conditioning for example) to see how it is performing and when it is time to do maintenance.
The results will help you identify what kind of energy efficiency measures to take.
2) Perform service when needed.
A lot of the equipment used within a telecom site (for example air-conditioning units, diesel power generators, etc.) requires regular service to operate reliably. Telecom sites are often serviced according to a pre-determined service schedule. As site visits are costly, we may be able to reduce the service costs if we only send the service team to sites that actually need service.
The challenge is to know when service is needed at each individual site. By analyzing the operation of equipment remotely, we are able to understand equipment health and more efficiently schedule service visits in the field.
3) Increase lifetime of batteries
Batteries have a limited lifetime which depends greatly on how they are operated as well as the surrounding temperature. With a temperature that is just a couple of degrees higher or lower than the optimal operating temperature, the lifetime of batteries is significantly reduced. And since batteries are expensive, this can generate substantial savings.
Normally, an FCU in combination with an air-conditioning unit is installed to regulate the temperature on site. Outdoor temperature fluctuations, equipment failure or even a door that has not been properly shut, will affect the temperature at the site and thereby generate unnecessary energy consumption. By recording the temperature at each site and monitoring and configuring temperature set-points remotely, we can assure an optimal climate inside the BTS and extend battery lifetime.
4) Improve reliability and operation of diesel power generators
Diesel power generators are often used for back-up power at telecom sites. In rural areas, the luxury of a reliable power grid might not be present, and in such cases the diesel power generator acts as the main source of power, occasionally combined with renewable energy sources, such as wind- or solar-power.
A great percentage of generator failures can be avoided by simply analyzing the basic operational parameters, such as fuel levels, battery levels, oil-pressure and coolant temperatures.
Service of a power generator is normally carried out at certain intervals, for example after operating the generator for a certain number of hours. By being able to see the operating hours remotely, we are able to make a decision of when to send a service engineer to the site.
Like a car that has been parked for an extended period, a generator engine that has not run in a long time is likely to have start-up problems. For back-up power generators that are not operated very often, it is important to regularly perform test starts. Remote test starts can be made with a remote monitoring solution that has control capabilities and is connected to the generator controller. With a simple action such as a remote test run, we are able to increase the likelihood of the generator working the day there is a power outage and the generator needs to perform.
A well-maintained generator operates better and with lower costs as unplanned operating disturbances often means substantial expenses.
5) Minimize fuel theft
Fuel theft can be a significant problem and reports have suggested that in certain regions, as much as 40% of the fuel disappear before it is used.
Avoiding fuel theft completely might be difficult since it is often stolen a bit at a time; during transportation, at fill-up, or at the telecom base station. However, a remote monitoring system that connects to a fuel sensor can be used to ensure that the right amount of fuel is delivered at a refill. By using an intelligent level sensor, it is possible to track the fuel level of the tank. The fuel sensor can be calibrated to sense a full tank and by knowing this we can verify that the tank is properly refilled. A good fuel level sensor is able to detect variations down to 3-5 liters.
An abnormal decrease in content may be detected and indicate that the fuel is being stolen. With a remote monitoring system that supports alarms, a notification is sent immediately as the theft occurs. Even if it might be hard to catch the thieves, we are at least aware that the fuel has been stolen and we can schedule a refill to ensure the generators have the fuel needed to operate.
Tracking the level of fuel in a tank remotely increases our awareness of what happens to the fuel on site and helps us understand when theft occurs. In some cases, where organized theft is common, this may help detect patterns and take action.
Remote monitoring puts you ahead of the game
Modern remote monitoring technology enables us to get instant access to data from equipment in the field and take action based on the information. This enables us to have full control 24/7 and creates instant awareness of any operational issues. Any modern telecom base station will quickly benefit from getting remote, online access to all passive equipment.
Images:
All passive equipment on a base station can be monitored and controlled remotely giving the service team access to the site 24/7.

With a laptop or smartphone, you can access your site from any location.

