www.industryemea.com
07
'22
Written on Modified on
Digitalization in the railway industry
Public transport has changed a great deal within the past ten years, with urban mobility undergoing a huge transformation. Digitalization and innovation have been behind many of the exciting changes to the ways in which we live and move. As digital evolution moves quickly, each new development puts us closer to the human-centred approach that the sector must remain focused on - By K.A. Gerardino.
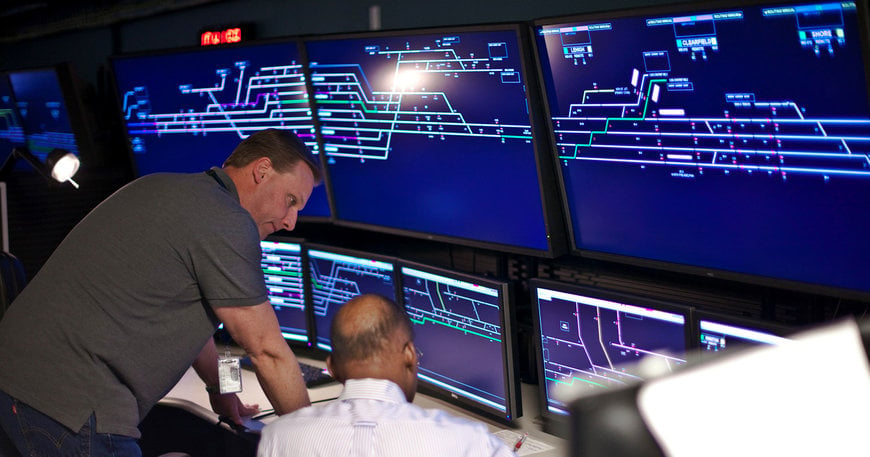

Thus, digitalization is driving new technologies in the railway industry. According to ReportLinker, the global digital railway market size is expected to reach US$103.7 billion by 2028, rising at a market growth of 9.2% CAGR during the forecast period.
The number of passengers using trains has dramatically increased during the past few years in many different nations. Railway operators require a variety of digital railway solutions, such as traffic management tools, passenger information systems, and passenger analytics, to effectively manage the passenger traffic and deliver high-quality transportation services to an increasing number of passengers. These solutions improve client travel experiences, while boosting the effectiveness of railroad operations.
Although the building of trains and how it is used have not changed, it is certainly altered the way we think about rail operations and maintenance. The goal of digitalization in the railway industry is to provide a more dynamic, responsive, and functional railway for rail passengers in the digital era.
Key factors driving growth
Increasing urbanization and widespread digitalization across the globe are among the key factors driving the growth of the market. The growing population and rising expenditure capacities have augmented the demand for personal mobility across the world. Consumers are increasingly adopting public transportations, such as high-speed trains and metros to commute and avoid congestion on the road.
Furthermore, the demand for dynamic and swift transportation systems by the rolling stock industry is also providing a boost to the market. Developing nations are extensively dependent on efficient asset and fleet management systems for remote diagnostics, asset planning and tracking services over long distances.
Additionally, the integration of automation and the internet of things (IoT) technologies in railway systems is positively impacting the market growth. Railway systems are being combined with big data analytics solutions to control and manage the communication systems, which assist the operators to identify malfunctioning components and prevent breakdowns. Moreover, the implementation of favourable government policies supporting the emerging trend of smart cities is also projected to drive the market in the upcoming years.
Hitachi Rail offers PTC onboard system and digital railcar telematics
Trends influencing rail Industry
In the last two decades, transit companies around the world are implementing new technologies to make passengers’ journeys more comfortable. Metro and other major public transport systems have progressed from simple mass transportation services to integrated public transport providers. Other than transporting passengers between origins to destinations, these public transport systems continue to embrace evolving digitalization for the provision of services, such as security, customer service assistance, and operational support.
As railways expand, investment in new technologies will be needed to monitor thousands of miles of tracks so that humans do not have to. A major focus will be using data and artificial intelligence (AI), IoT to the incorporation of connectivity innovations. Here are the top trends in the rail and railway industry, according to Railquip:
Autonomous Trains: Autonomous trains have emerged as effective innovations to enhance city utilization, and reliability, in the rail industry. In essence, innovations like real-time data transmission systems and advanced sensor technology have made autonomous trains a great possibility.
Stakeholders in the railway industry have adopted automatic train control systems to enhance the flow of technical information while minimizing technical errors and instilling confidence among passengers. For instance, the modern rail system has resorted to automated innovativeness to take control of emergencies.
IoT: The industry has adopted IoTs to enhance the reliability and safety levels of the railway infrastructure. IoT analytics have enabled stakeholders in the industry to embrace data-driven operations for fleet control and foster rail operational efficiency. Similarly, data-driven monitoring systems have helped train operators to reduce delays by tracking system failures.
High-speed rails: Speed has remained a crucial issue for the global rail and railway industry. The High Speed 2 (HS2) project in the UK laid a great foundation for high-speed railway systems. Other European economies like Denmark have followed the same mechanism to adopt their first high-speed railway infrastructure. It is expected that global economies will embrace this trend moving forward.
AI: AI has emerged as the new order in the rail and railway sectors. From emergency notification and asset management to predictive maintenance, AI is the way to go. The emergence of start-ups like The Train Brain (Sweden) has helped stakeholders in the industry incorporate AI models like neural networks, deep learning algorithms, and GPS data to minimize delays and enhance train scheduling operations. The future in the rail and railway industry remains bright as stakeholders grip AI innovations to initiate data-driven traffic planning.
Decarbonization: The rail and railway sectors are playing an active role in decarbonizing our cities as it offloads the long-standing climate change blames. Both train operators and railway infrastructure managers have sought and implemented energy-saving strategies. For instance, long-distance operators like Poland-based PKP Intercity installed over 350 energy meters on their trains. Still, other carriers have resorted to the use of renewable energy. For instance, Wien Hauptbahnhof, Vienna’s main train station, has laid plans to install its heating facilities with geothermal systems.
Train stations in key economies have made massive leaps in their efforts of increasing their green energy investments as they rush to meet the requirements to decarbonize the European Union‘s railway sector by 2050. For example, ProRail, a Dutch railway infrastructure manager, has started its solar installation mission at train stations to double the volume of green energy used. However, the rail and railway sector in Europe will have to do a lot to meet this ambitious goal as other continents replicate the strategies that they have used.
Increased Connectivity: The industry has exploited avenues that will enhance reliability and high performance through efficient connectivity. Today, the rail and railway sectors are steadily implementing modern mobile communication systems and low-latency communications to foster inter-partner connectivity.
As 5G technologies take shape in diverse global platforms, there is a tendency that the sector will experience massive advancements of optoelectronic ground-to-vehicle media aimed at fostering autonomous connectivity. Further, the rise of communication-based train control mechanisms has enabled effective asset monitoring and traffic management.
Consumer Experience: Stakeholders in the rail and railway industry have made great efforts to enhance their customer experiences. Today, trail hotel experiences, automatic ticketing, and video surveillance activities have taken center stage in the industry. Video surveillance devices have not only helped in optimizing passenger load in trains but also theft detection.
Similarly, the industry has taken advantage of mobile applications to automate price comparison and issuance of tickets. Stakeholders have taken advantage of boarding innovations to streamline their last-booking operations, seat assignment, and identification control.
This trend will matter more in the rail industry as the industry continues to adopt more sustainability elements as it moves forward. Recall that consumer experiences in the rail transportation industry will matter based on direct experiences while using these rail services. At the same time, the consumer experiences related to the rail transportation industry will also count on larger matters that focus on sustainability, efficiency, and overall effectiveness.
Big Data Analytics: The industry has taken hold of big data analytics to foster train communication, passenger information systems, and asset management.
Companies have deployed smart sensors to gather and analyse millions of data sets to enhance the safety and reliability levels of the railway infrastructure. Big data innovations have presented the stakeholders in this industry to predict operational failures and schedule the necessary repairs.
Big data analytics within the rail sector will help to improve the rail network and general transportation in several ways. Indeed, more data and technology can bring about more improved options in expansion, current operations, and how the transportation sector looks at infrastructure in railroads.
Cybersecurity Advancements: Digital advancements in the rail and railway sector have allowed companies to implement futuristic approaches in their predictive maintenance operations by investing in platforms that allow for real-time data collection and analysis.
The results obtained in these systems play a great role in revealing the chances that a particular plan will face operational failures. In this case, sensors send the required pieces of data back to the central control system that tracks the suitability of the train (or other movable railway systems) to perform the assigned roles.
The rail and railway industry has adopted a transformational gear o enhance its consumer experiences while reducing the associated costs of operation. There is a tendency that the industry will adopt a more innovative viewpoint as we move towards 2050.
Like other sectors, the rail and railway industry consider mergers and acquisitions as the most effective strategies to transform, consolidate, and grow their operations. Now, it is only fair to adopt the wait-and-see attitude as things take shape in the industry.
These are a few of the many compelling trends taking place within the transportation and railroads segment. From added technologies to safety measures, to demand, research, and maintenance as well as innovation, it is an important part of the transportation infrastructure and is likely to stay relevant over the next few decades as it continues to grow at a modest rate.

Huawei introduced FRMCS solution at InnoTrans 2022 and at 9th Huawei Global Rail Summit held in Berlin
Partnerships, collaborations
The impact of digitalization is a game-changer on all activities in the rail transport sector. Through the engagement of appropriate digital transformation partnerships and collaborations, public transport operators can achieve certain cost reductions, service quality enhancement, improved reliability, and the most optimal use of their physical assets. Below are recent strategies deployed in the digital railway market:
ABB came into a partnership with Red Hat, an American software business in August of 2022. With this partnership, companies aimed to permit enterprises utilizing ABB’s process automation and industrial software to scale flexibly and rapidly utilize Red Hat’s dominating enterprise platforms and application services developed on Red Hat Enterprise Linux. Moreover, the partnership allows containerization and virtualization of automation software with Red Hat OpenShift to deliver developed flexibility in hardware deployment, optimized as per application requirements. Wabtec Corp. joined hands with Deutsche Bahn, the second-largest transportation business in the world in May 2022. Through this collaboration, the companies aimed to optimize the maintenance and operation of Wabtec equipment on council Deutsche Bahn trains.
Additionally, the companies would collaborate as a joint Steering Committee for various projects to improve the availability, reliability, and life cycle of Wabtec tools established on Deutsche Bahn trains. In April 2022, Thales signed a memorandum of understanding with SMRT Trains, a rail operator in Singapore. With this agreement, the companies would transfer engineering knowledge and rail expertise in diverse sectors and utilize digital technologies such as AI and data analytics to release the full capabilities of the diagnostic data readily general within the current signalling and rail systems.
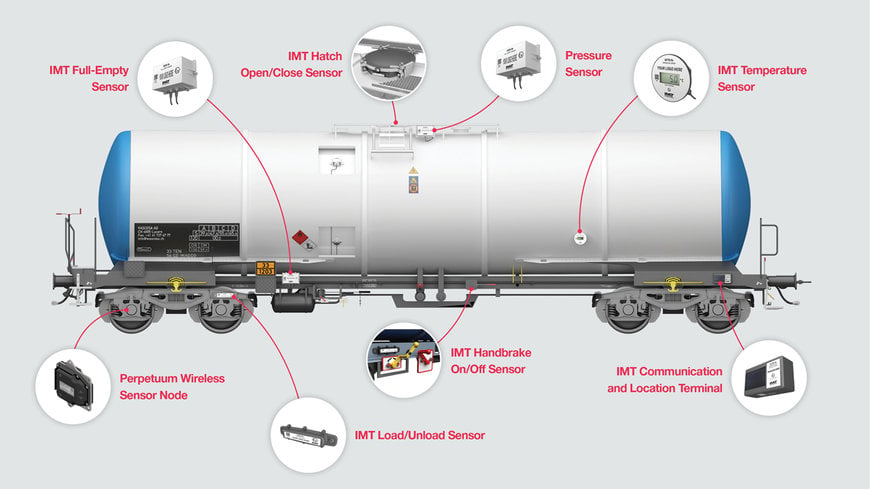
Hitachi Rail formed a partnership with Intermodal Telematics, a leader in the development of monitoring sensors and telematic solutions in January 2022. Through this partnership, the companies aimed to adjoin IMT’s pioneering monitoring sensors to Hitachi’s living digital freight service. Additionally, the agreement would permit Hitachi to deliver rail freight companies across the world a solution that delivers real-time monitoring to enhance safety and effectiveness.
Product Launch and expansions shaping the future of railway service
2022 has seen a steady stream of product launches and expansions from some of the world’s largest railway technology manufacturers. These new products will greatly benefit the global railway industry value chain, helping to further alleviate the shortage, generate new jobs, create increased demand for fab equipment, and drive innovations.
Technology firm Huawei has introduced the Future Railway Mobile Communication System (FRMCS) solution to drive a digital shift in the railway sector. The solution was unveiled at InnoTrans 2022 and the 9th Huawei Global Rail Summit held in Berlin, Germany. FRMCS will enable functions that include the use of train-to-ground wireless services for train control and dispatch, railway operations and maintenance (O&M), and railway internet of things (IoT). The solution will also help enhance train operational efficiency and safety, according to the firm.
Wabtec introduced Precision Dispatch System. The new Wabtec Precision Dispatch System is developed to move trains safely and effectively around the rail network in both signalled and dark territory, as well as deliver complete transparency of network requirements and monitor all devices in the network. Additionally, precision dispatch analyses data collected from all rolling stock and Positive Train Control and wayside device assets. Hitachi Rail launched PTC onboard system and digital railcar telematics. The new Positive Train Control is an onboard system is an Interoperable Train Control solution for cargo railroads and commuter rail operators. Thales announced the launch of its prevailing Train Protection and Warning System (TPWS) Mk4 Single Cab Control Unit.
The new TPWS Mk4 is comfortable to fit and run with current systems in both dual and single cabs, with no requirement to change anything under the vehicle, TPWS Mk4 is a concise, cost-effective advancement that demands minimal staff training, whilst providing interoperability with European Train Control System. Thales presented the Robust Train Positioning System, a system that delivers precise train positioning data and a digital map. The new Robust Train Positioning System is focused on increasing safety by utilizing a mixture of sensors that gather crucial data on train positioning, which is integrated with a digital map of the track, supplying precise and constant positioning results for train drivers and other attendants.
Railway electrification systems rely on a steady DC supply to both power their DC motors and the control/energy circuits. These DC-traction systems are more energy efficient than their coal, gas,or diesel-based counterparts while also reducing CO2 emissions. P-DUKE has offered RHKW (3W/6/10W), RHMW (20W), and RHDW (40W) series DC-to-DC converters are ideal for 72V, 96V, and 110V railway inputs and meet EN 50155, EN 61373, and EN 445545-2 railway standards as well as the IEC/UL/EN 62368-1 standard (with reinforced insulation) for electrical equipment. They are tested for vibration and shock with a wide operating temperature from -40°C to +105°C and are operational at 5000 meters for rolling stock that may run through mountainous regions.
Railway-focused acquisitions and mergers to deliver improvements
Although massive manufacturers dominate the global train construction industry, acquisitions and mergers are breaking into the railroad business by providing digital and electronics offerings that can be installed on railcars and the railways.
In June 2022, Wabtec Corp. completed the acquisition of Collins Aerospace’s ARINC rail solutions, a supplier of intelligence-based rail dispatch and back-office solutions. Through this acquisition, ARINC’s rail solutions systems, associated with Wabtec’s digital and electronics offering, would boost the industry’s travel of rail optimization. Wabtec also completed the acquisition of Trimble’s Beena Vision business, a producer of machine vision-based wayside inspection systems in April 2022. This acquisition would expand Wabtec’s unparalleled digital and electronics offering, improving its capability to advance wayside train condition monitoring, along with supply chain and logistics technology for railroad consumers across the world. In addition, Wabtec took over Masu, the railway friction industry in January 2022. This acquisition would reinforce its established base, as well as develop its brake product offering. Additionally, Wabtec would also be capable to toughen its position as a foremost rail manufacturer in India.

RHDW series of railway DC-to-DC converters from P-DUKE
5G to revolutionise the railways
Fifth-generation (5G) wireless communications promise to shape the future of the railways by offering ultra-low latency and ultra-high reliability. The 5G FRMCS will overleap the 2G cellular rail standard Global System for Mobile Communications–Railway (GSM–R) standard that is still running in trains and traffic control centers in over 35 countries around the world today.
FRMCS, which is based on the standalone version of the 5G NR spec, is expected to be completed by the end of 2022. The niche specification will have access to harmonized frequencies at 900 MHz and 1900 MHz. This is to ensure that train operators’ rail command and control systems will remain interoperable when the transition from GSM–R to FRMCS takes place.
FRMCS is an umbrella standard covering all future rail use cases requiring a mobile communication system. Prominent examples include the European Rail Traffic Management System, where FRMCS will replace GSM-R, as well as internet of things (IoT) based maintenance or passenger information over the internet.
The latest thinking of the International Union of Railways and the European Railway Agency shows a clear preference towards 5G as the basis for FRMCS, a choice supported by many major European railway operators.
Communications security is a major issue for the rail industry. The GSM–R standard uses an outdated security technology, the A5/1 steam cipher, which was first broken in 1999. This will change with the arrival of the secure and reliable FRMCS system in 2025. The fact that you can use a single link will spur so much infrastructure, as well as improve the throughput and the latency for [all] types of applications. It will unlock massive opportunities for operators and passengers.
Nokia claims that FRMCS will lead to simplified rail maintenance, more remote control of station lighting and CCTV, and eventually automated train operation, among other advances. Notably, other hardware vendors, such as Ericsson and Huawei, are equally keen to promote FRMCS.
5G is not just about providing more bandwidth to users – it is also designed for industrial uses, especially automation and sensor communications.
Sensors will be employed for monitoring tracks, rolling stock, power systems and environmental conditions. 5G will enable all this data to be connected in real-time. When combined with software analytics and machine learning, this will enable railway operators to carry out preventative maintenance, predict failures, and anticipate floods and other events that could interrupt services.
The higher bandwidth made possible with 5G will allow much greater usage of high-quality video for security, communications between operational personnel, improved situational awareness during emergency events, drone inspections, and a host of other applications that generate video and/or high amounts of data.
Using IoT data to predict maintenance requirements will increase the availability and productivity of rail assets, as well as [facilitate] higher standards of protection, not only from cybersecurity attacks but also physical threats.
Conclusion
Railways are already one of the greenest methods of transport, and operators will continue to capitalise on this in the coming year. In addition to saving fuel and reducing costs for operators, technology will also boost safety, particularly when it comes to the implementation of automatic train control. Increased automation in general will lead to new considerations about how operators optimise their plan for the future.

